CNC Machining: A Comprehensive Glossary
Welcome to our website! Here you will find a detailed glossary of the key terms and concepts related to CNC machining. This glossary provides you with an in-depth look into the world of computer-controlled manufacturing and helps you better understand the technical terminology.
What is CNC Machining?
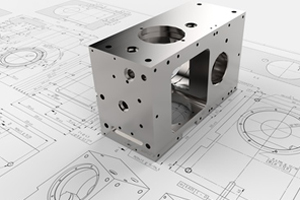
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process where computer-controlled machines perform precise and repeatable movements to process materials such as metal, plastic, or wood. CNC machines are used in numerous industries, from automotive to aerospace, and enable the production of complex parts with high accuracy.
Key Terms in CNC Machining
Axes: In CNC machining, axes refer to the directions in which the tool or workpiece moves. The most common machines have three axes (X, Y, Z), but there are also machines with five or more axes for more complex operations. Machines with additional axes provide greater flexibility and precision when machining complex geometries.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): CAD software is used to create detailed 2D and 3D models of the parts to be manufactured. These models serve as the basis for CNC machining and are imported into CAM software.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): CAM software is used to program CNC machines. It converts CAD models into machine-readable instructions and optimizes the machining processes. The CAM software generates the G-code that controls the movements and operations of the CNC machine.
CNC Lathe: A CNC lathe is a machine primarily used for turning workpieces. It rotates the workpiece and uses fixed cutting tools to remove material and produce the desired shape. CNC lathes are commonly used to manufacture cylindrical parts such as shafts and bushings.
CNC Milling Machine: A CNC milling machine uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece. It can operate in various axes to create complex geometries. CNC milling machines are versatile and used to produce parts with intricate contours and shapes.
G-Code: G-Code is the programming language used by CNC machines. It consists of commands that control the machine’s movement and functions, such as positioning, feed rate, and cutting patterns. G-Code is the standard in CNC machining and allows precise control over machine operations.
HSM (High-Speed Machining): High-speed machining is a technique where very high cutting speeds and feeds are used to reduce machining time and improve surface quality. HSM requires specialized tools and machines capable of handling high speeds and loads.
Zero Point: The zero point is the starting point for all machining operations on a CNC machine. It serves as a reference point from which all movements and positions are measured. The zero point is established during machine setup and is critical for machining accuracy.
Post Processor: A post processor is software that converts CAM output data into specific G-code formats understood by a particular CNC machine. The post processor takes into account the unique characteristics and capabilities of the machine to ensure efficient and error-free machining.
Tool Change Mechanism: This is a mechanical system that allows the CNC machine to automatically switch between different cutting tools to perform various machining operations without interrupting the process. Tool changers significantly increase the efficiency and productivity of the machine.
Feed Rate: The feed rate is the speed at which the cutting tool moves through the material. It is often measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min) and has a major impact on machining quality and time. The optimal feed rate depends on the material, cutting tool, and specific machining operation.
Spindle: The spindle is the rotating component of the CNC machine that holds and drives the cutting tool. The spindle speed significantly affects the efficiency and quality of the machining process. CNC machines can be equipped with high-speed spindles to meet the demands of high-speed machining.
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): CMM machines are used to verify the precise dimensions of machined parts. They use a tactile probe to measure and compare the dimensions and positions of features. CMM measurements are crucial for quality control and ensure that the machined parts meet specifications.
Trochoidal Milling: A machining process where the tool moves along a spiral path. This reduces cutting forces and improves tool life and surface quality of the workpiece. Trochoidal milling is especially useful for machining hard materials and deep cavities.
Adaptive Machining: Adaptive machining adjusts machining parameters in real-time to maintain optimal cutting conditions and maximize efficiency and quality. This technology uses sensors and advanced algorithms to continuously monitor and adjust machine operations.
Material Removal Rate: Material removal rate refers to the amount of material removed from a workpiece during a specific period. It is an important parameter for evaluating the efficiency and productivity of a CNC machining process.
Roughing and Finishing: Roughing is the initial machining step where large amounts of material are removed quickly to create the rough shape of the part. Finishing is the subsequent step where smaller amounts of material are removed to achieve the final shape and surface of the part with high precision.
Workpiece Clamping: The method used to secure the workpiece on the CNC machine. Proper workpiece clamping is crucial for machining accuracy and safety. There are various clamping systems such as vises, collets, and magnetic clamping systems.
Machine Stiffness: The stiffness of the CNC machine affects machining precision and quality. A rigid machine minimizes vibrations and deformations that can occur during the machining process, leading to more accurate results.
This glossary covers some of the key terms in CNC machining. We hope it helps you gain a better understanding of this complex and fascinating manufacturing process. If you have any further questions or need more information, feel free to contact us.